Network Switch: Managed vs. Unmanaged Switches Compared

Introduction
A network switch is equipment that allows two or more IT devices, such as computers, to communicate with one another.
A network switch connects devices typically within a local area network (LAN) and forwards data packets to and from those devices. Unlike a router, a switch only sends data to the single device it is intended for (another switch, a router, or a user’s computer), not networks of multiple devices.
Connecting multiple IT devices creates a communications network. The network can share computing, print, server, file storage, Internet access, and other IT resources.
Selecting the right network switch is a crucial decision that impacts your business network’s reliability, security, and scalability.
When selecting the correct type of switch to meet your needs, one consideration is whether to use a managed or an unmanaged switch. The key difference is the amount of control you have over the switch’s settings.
Unmanaged switches are designed to plug in and run with no configurable settings. They are okay to use in small networks with only basic needs. Managed switches, however, are fully configurable and customizable and provide a range of performance data. Those attributes make them more suitable for more extensive networks and networks supporting critical activities.
What is a Network Switch?
As we’ve discussed, a network switch is a hardware component that relays data from networks to the destination endpoint through packet switching, MAC address identification, and a multiport bridge system. Network switches are a vital component of all networks as they link devices that share resources.
In how they handle data transmissions, switches are different from hubs and routers, which are also network devices.
Hubs are essential network devices that act as multiport repeaters. This means they receive data from one port and broadcast it to all other connected ports.
Switches are more intelligent than hubs. They learn the MAC addresses of devices connected to their ports and forward data packets only to the intended recipient’s port.
The functions of the three devices are all quite different from one another, even if sometimes they are all integrated into a single device.
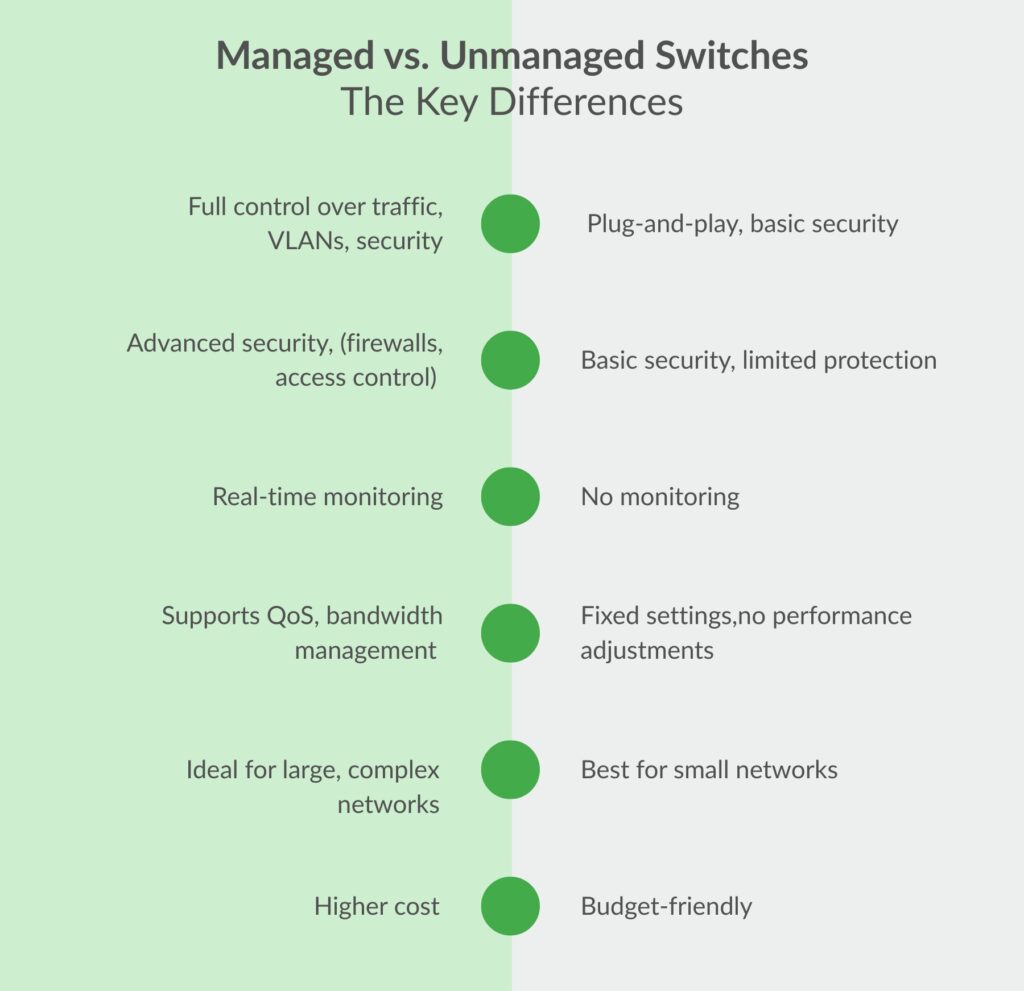
Managed vs. Unmanaged Switches: Key Differences
| Feature | Managed Switch | Unmanaged Switch |
| Control & Customization | Full control over traffic, VLANs, and security policies | Plug-and-play, no configuration needed |
| Security Features | Advanced security (firewalls, access control) | Basic security, limited protection |
| Network Monitoring & Troubleshooting | Provides real-time monitoring, SNMP support | No monitoring capabilities |
| Performance Optimization | Supports QoS, bandwidth management, and load balancing | Fixed settings, no performance adjustments |
| Scalability | Ideal for large, complex networks | Suitable for small networks with minimal management needs |
| Cost | Higher cost due to advanced features | Lower cost, budget-friendly option |
What is a Managed Switch?
A managed switch is a switch that allows IT admins to configure, manage, and monitor traffic.
Key Features:
✅ VLAN (Virtual LAN) support for network segmentation.
✅ Quality of Service (QoS) for prioritizing critical data.
✅ Security features like MAC address filtering and port authentication.
✅ Remote monitoring via SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol).
Managed switches are best for enterprises, data centers, and growing businesses with complex network needs.
What is an Unmanaged Switch?
An unmanaged switch is a simple plug-and-play switch that requires no configuration.
Key Features:
✅ Auto-negotiation for easy setup.
✅ Basic traffic forwarding without interference.
✅ Cost-effective and easy to deploy.
Unmanaged switches are best for small offices, home networks, and temporary setups.
Pros & Cons of Managed vs. Unmanaged Switches
✅ Pros of Managed Switches
✔ Greater control over network traffic.
✔ Enhanced security features for data protection
✔ Better performance optimization with quality of service.
✔ Supports network expansion and remote management.
❌ Cons of Managed Switches
✘ Higher cost.
✘ Requires IT expertise to configure and manage.
✅ Pros of Unmanaged Switches
✔ Easy to set up—plug and play.
✔ Affordable, lower upfront investment.
✔ Reliable for small-scale networks.
❌ Cons of Unmanaged Switches
✘ No traffic control or performance optimization.
✘ Limited security, vulnerable to cyber threats.
✘ It cannot be remotely monitored or configured.
Which Switch Is Right for Your Business?
Unmanaged switches are often seen in minimal, uncomplicated networks with only a dozen or so devices connected and without critical requirements for security and availability.
Choose an unmanaged switch if:
• You run a small business with minimal networking needs.
• You need a simple, cost-effective solution.
• There’s no requirement for network customization.
With the flexibility and control they provide, managed switches are a must for networks where reliability and security are critical. Typically, such networks power enterprise-level businesses, government agencies, universities, and healthcare organizations.
Choose a managed switch if:
• Your business needs high security and performance.
• You have an extensive network with multiple devices.
• IT teams need remote access and monitoring tools.
While managed switches cost more than unmanaged switches, the range of models available means that businesses of all sizes can choose between different levels of complexity and cost.
Conclusion
To recap, managed switches have more capability than unmanaged switches, but they also require a skilled network administrator or engineer to make the most of them. A managed switch enables better control of networks and the moving data frames. On the other hand, unmanaged switches allow connected devices to communicate with one another in their most basic form.
The key differences between managed versus unmanaged switches are the following:
- Control and performance
- Features
- Cost
- Security
- Scalability
As mentioned, managed switches are more expensive than unmanaged switches, as they require software patches, updates, and, often, a skilled professional for implementation. That said, complex networks consisting of servers, wireless access points, PCs, and IoT devices usually necessitate the configuration options on managed switches.
The right choice often depends on the size of your business, security, and IT expertise.
Whether you want to add managed or unmanaged switches to your network, explore Plow Networks’ network services for tailored networking solutions and expert guidance.
Explore more on:





